EFFICIENT (EFFectIve food Chain IntervENTion) Protocol
The interactive Excel-based tool guides the user through 6 phases that can be implemented in sequence. The phases include 1. Scoping phase, 2. Flow phase, 3. Focus phase. 4. Measurement phase (optional), 5. Causes phase and 6. Interventions phase. The result of the first phase forms the starting point for the second phase, and so forth. An interested user also has the option to focus on a single phase or a number of selected phases of the protocol.
What type of insights does the methodology generate?
- What are the hotspots of FLW in the supply chain, the critical loss points, root causes of FLW, and potential interventions for my supply chain's FLW issues?
What type of questions does the methodology help respond?
- A food flow diagram including the activities, volumes and destinations of food flows and side streams.
- Data per supply chain link, such as activities, destinations of side streams, FLW volumes and percentages, economic losses, lead times, and input and output volumes.
- A root cause tree to help identify the root causes of the critical loss points identified within the supply chain.
- Long list with potential interventions and decision support to decide upon an effective intervention.
Links to publications
Links to video's
Case example
Case context
As part of a project implemented in Bangladesh, three value chain analyses took place using the EFFICIENT protocol. The aim of these analyses was to develop a strategic action agenda to reduce and mitigate FLW within three key commodities (onion, beef and mango) for the four city corporations in Dhaka.
As part of the work, and due to the lack of FLW data available, initial efforts focused on collecting new primary data and performing a value chain analysis together with local stakeholders. Detailed insights generated during the different phases of the onion value chain analysis are provided below.
Users and approach for onion value chain analysis case
Although stakeholders are aware of the challenges and bottlenecks in the onion supply chain, they do not know where to start to improve the food supply chain and reduce FLW. The EFFICIENT Protocol was utilised as it requires limited resources and time and as it complied with the need to monitor FLW, identify FLW hotspots along supply chains stages, root causes for FLW, and assess possible supply-chain interventions.
Insights from the scoping phase: The scope of this case study includes onions produced in Bangladesh destined for the domestic market. It includes all actors in the onion supply chain, from the moment of harvest up to and including retail, foodservice and mobile vendors. The geographical regions in scope of this analysis included the main onion production ar
Insights generated through the EFFICIENT protocol
Insights from the scoping phase: The scope of this case study includes onions produced in Bangladesh destined for the domestic market. It includes all actors in the onion supply chain, from the moment of harvest up to and including retail, foodservice and mobile vendors. The geographical regions in scope of this analysis included the main onion production areas and the four Dhaka city corporations.
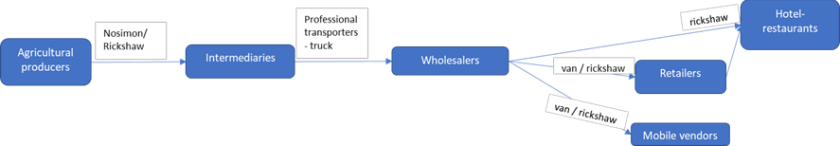
Insights from flow phase
Insights from focus phase
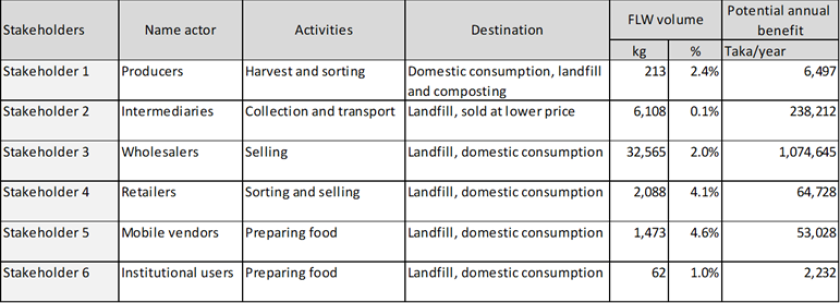
The FLW hotspot in the onion supply chain is found at the stage of the wholesaler. Wholesalers face the largest volumes and percentages of FLW from rotting and damaged onions, as highlighted in the table below.
The protocol focusses on FLW, not on FL only. Also in this example, wholesale was selected as hotspots. In the FAO definition this is FW, not FL
Insights from root causes phase
Although the hotspot for FLW was identified at the wholesaler stage, insights from the root cause analysis revealed that the root causes of FLW include improper harvesting and curing, lack of proper storage, high moisture content and improper handling during transport. The root causes of FLW in onions originate at an earlier supply chain stage than the FLW hotspot.
Insights from intervention phase
Insights from the analysis identified that the most promising intervention to (partly) address the root causes of FLW in the onion supply chain is to invest in sufficient and effective storage capacity and good practices during harvesting, curing and handling.
Do you have questions about using this tool?
We are happy to help. Please fill out the contact form and we will get back to you soon.
Photo: Kobby Dagan, Shutterstock.com
